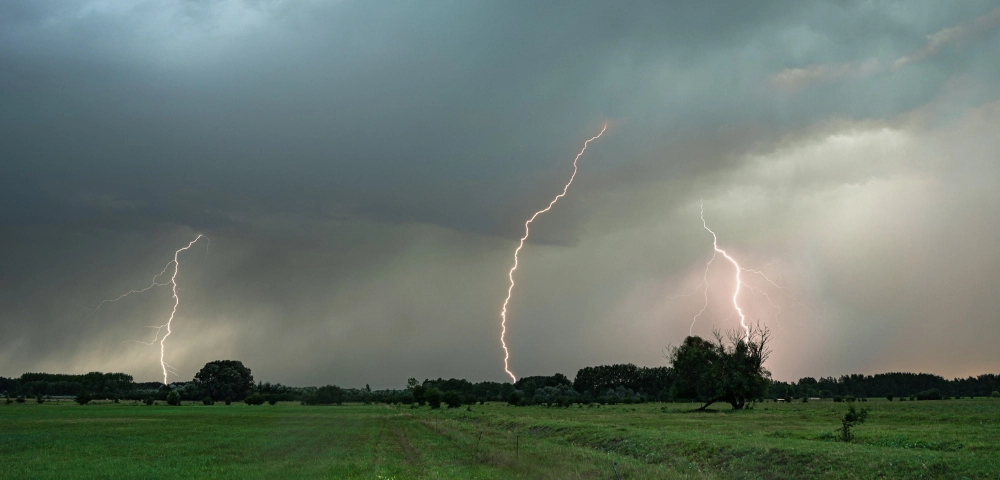
What Are Thunderstorms?
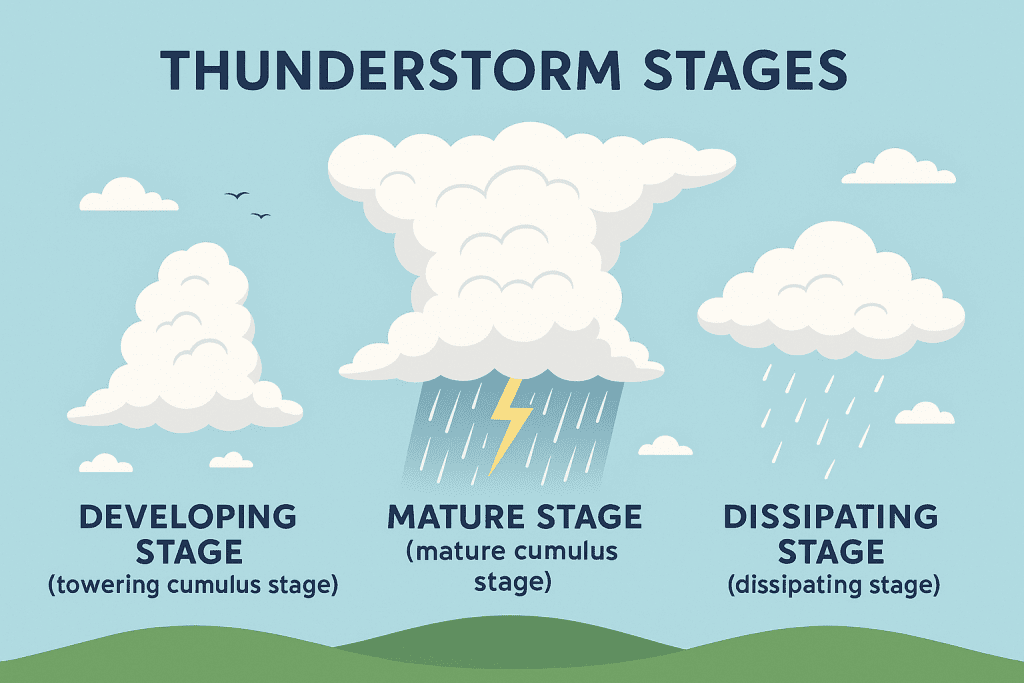
Thunderstorms are special weather phenomena containing both thunder and lightning. Thunderstorms bring risks such as hail, lightning, wind gusts, and flash floods. These storms are comprised of three stages; the developing stage (also called the towering cumulus stage), the mature stage (also called the mature cumulus stage), and the dissipating stage.
How Do Thunderstorms Form?
The Developing Stage (Towering Cumulus Stage)
As the Earth’s surface warms, convection begins, carrying warm, moist air upward. Strong rising currents quickly lift this air into the higher levels of the atmosphere.
As air cools, the water vapor condenses to form clouds. The release of latent heat fuels the storm, causing the cloud to grow and extend up to the higher levels of the atmosphere. At these altitudes, temperatures are well below freezing. Since the storm is still developing, no precipitation or downdrafts are observed.
The Mature Stage (Mature Cumulus Stage)
This is the most intense stage of the storm. Lightning, turbulence, and strong winds occur. Heavy precipitation composed of large raindrops is observed. The precipitation carries cold air downward, and when it reaches the ground it spreads outward; this phenomenon is called a downburst.
Inside the cloud, the presence of ice crystals, supercooled liquid water droplets, and graupel (particles formed when water droplets freeze onto other particles within the cloud) creates the conditions for electrification. While lighter ice crystals become positively charged, the heavier graupel particles carry negative charges. This separation of charges within the storm leads to lightning.
Strong updrafts and downdrafts inside the cloud (especially during the mature stage) continuously transport water droplets up and down. Rising droplets freeze in supercooled regions, partially melt as they descend, and upon being lifted again, refreeze and add new layers. After being repeated many times, this process causes smaller ice particles such as graupel to grow layer by layer into hail. Once the hailstones become heavy enough, the updrafts can no longer hold them, and they fall to the ground.
The Dissipating Stage
As downdrafts become dominant, the upward flow of warm and moist air that fuels the storm is cut off. The cloud begins to lose its energy source, precipitation decreases, and winds weaken. Eventually, the storm breaks apart, leaving behind only scattered clouds and residual moisture. At this stage, the risk of lightning still persists.


